2.3.1 Experimental Study on Macromolecular Dispersant D Concentration Conditions
The monomer droplets (about 10 μm) formed during the preparation of the polymerized toner are much smaller than those of ordinary suspension polymerization (hundreds of μm), and the monomer droplet/water interface is increased, and the macromolecular dispersant protective film is required to have sufficient strength. Thickness, in the polymerization process does not occur between the droplets and the merger, therefore, the concentration of macromolecular dispersant D must be doubled, but the concentration of macromolecular dispersant D is too high, it will cause difficulties in the late cleaning of the toner, so the dispersion of large molecules The concentration of agent D is such that a protective film of sufficient strength and thickness can be formed on the surface of the monomer droplets, and monomer droplets do not aggregate in the polymerization process. Reference [10], we select macromolecular dispersant D with a mass fraction of 0 3% 0 5% and 1% water content when the test (other components according to Table 1), at the same stirring speed and stirring speed, the dispersed phase droplet diameter is only related to the interfacial tension [7]: dpmax ∠γ 3/5 test test The interfacial tension of mixed monomers with a mass fraction of 0.3% 0.5% 1.0% of macromolecular dispersant D aqueous solution was 24.524.023.0 mN/m, and the diameter of the corresponding dispersed phase was 6.46.36.1 μm. This result indicates that the Molecular dispersant D mass ratio of 0 3% to 10%, dispersed phase droplets Difference is not great, it can be obtained whether the toner volume average particle size 10μm, depends on whether it occurs in dispersion polymerization, and polymerization.
Table 3 shows the powder particle size test results obtained in the same reaction conditions for 6 h under different macromolecular dispersant D concentrations: gsd=(d84/d16)/2
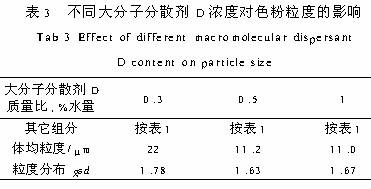
Toner particle size test results show that when the mass ratio of macromolecular dispersant D is 0.3% water, the formation of protective colloids on the surface of the monomer droplets is not sufficient to completely prevent the droplets from interspersing, and thus the toner particle size is larger. The molecular dispersant D mass ratio is 0.5% and 1% of the toner obtained similar particle size, observed by the microscope camera D mass ratio of 0.5% when the mixed system in the reaction process dispersed phase droplet diameter changes, the results show that basically no aggregation occurs, so determine the quality of D 0.5%
2.3.2 Experimental Study on Surfactant DY Concentration Conditions
Adding an anionic surfactant to the aqueous phase of the mixed system can greatly reduce the oil/water interfacial tension, and at the same time form an electric double layer effect at the oil/water interface, reducing the drop diameter of the monomer droplets and preventing the droplets from being condensed but the concentration exceeds The critical micelle concentration is easy to form an emulsion, and the final product is a latex particle size of 1 μm or less. Under a microscope, the mixed system is dispersed under the same homomixer, and the result shows that no anionic surfactant is added. In DY, the droplet size of the dispersed phase is significantly larger, indicating that the active agent concentration greatly exceeds the CMC value, resulting in a very fine (about 1 μm) monomer droplet with adsorbed emulsifier molecules on the surface, as well as an increased sol bundle with a diameter of about 4-5 nm. Therefore, select the DY concentration close to the CMC value, the experimentally determined mass fraction of 0.035%
2.4 Selection of Water to Oil Ratio
Increasing the ratio of water to oil does not harm the suspension polymerization itself, and the resulting particles become finer and the particle size distribution becomes narrower, but the utilization efficiency of the polymerizer decreases but the water ratio is too low, and the amount of water is not sufficient to fill the space between droplets or particles. Sudden increase in the viscosity of the suspension system, stirring, object flow and heat transfer difficulties, and even lead to out of control of polymerization This test selected water and oil ratio of 5:1
3 Conclusion
For the reaction system consisting of the basic formulation shown in Table 1, under the following dispersion conditions and dispersant concentration, the reaction system can achieve almost no disperse phase interpolymerization in the polymerization process and reacts at 85° C. for 8 to 10 hours to obtain a particle size close to 10 μm. Electrophotographic toner powder products: homogenizer stirring speed: 5000r/min (8.9m/s); homogenizer mixing time: 20min; reactor stirring speed: 800r/min (2.6m/s); macromolecular dispersant D Mass ratio: 0.5% water; surfactant DY mass ratio 0 035% water
Author: Duan Ying Feng Qiang east
Curtain Rod Solid Wood Finial,Wood Drapery Rods,Wooden Curtain Pole,Wooden Curtain Rods
HANGZHOU AG MACHINERY CO.,LTD , https://www.famourdecor.com