Exploration of metal barrel flanger (2)
There is also a horizontal double-head hydraulic flanger which is also a rolling type flanger. Its shape is similar to that of Figure 4. However, both the feed motion and the headbox feed movement are hydraulically completed, so the structure is simple in Figure 4 (with a simple hydraulic pump and hydraulic cylinder instead of a mechanical drive and feed device such as cam feed) . The main rotary motion is still driven by the motor to reduce the speed of the primary belt drive and the tooth drive transmission. It has a high degree of automation, good edge accuracy, smooth transmission, low noise, and is widely used abroad. In China, due to the fact that the leakage of hydraulic components has not been solved well and the price of hydraulic oil is high, it has also limited the extent that this type of burring machine is widely used in China.
Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of the operation of the simplest vertical single-head hydraulic flanger. The movement characteristic of the burring machine is that the barrel frame is actively rotated, and the two pressure rollers are rotated by the barrel frame during the burring process, and the feeding motion is realized by the radial translation of the inner pressure roller.
The working process of the machine is as follows: Firstly, the piston in the cylinder 8 is in the lowest position, and the tail plate 7 at the end of the piston rod is at the lowest position, and the barrel frame to be flanged can be placed on the tail plate. When the piston in the cylinder 8 is ascending, the tail tray 7 and the bucket frame are moved up until the upper end of the barrel frame contacts the axial positioning roller 4, as shown in the position of (a) in the figure. Then the main shaft 3 and the fixed spindle 3 are fixed in it. The upper turntable 5 rotates, and the bucket frame and the tail tray 7 are driven to rotate together. At this time, the outer pressure roller 1 is swung to the outer edge of the barrel mouth, and the inner pressure series 2 is translated to the outside of the barrel until the barrel is turned over. When the side is finished, see (6) in the figure.
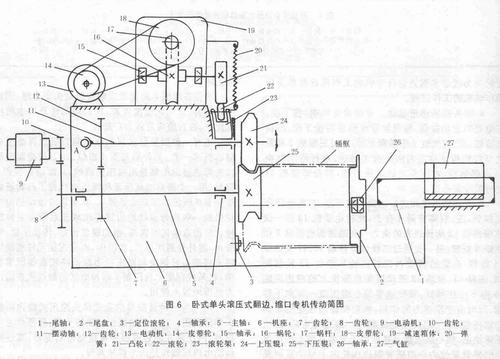
In addition to the cuffing process of the barrel, the hydraulic cuffing machine can also change the shape of the upper and lower presses, and can also complete the rolling and necking of the barrel (ie, the neck), also known as the shrinking process, and even At the same time, complete the integrated process of flanging, rolling ripple and necking. Figure 6 is a schematic diagram of the drive of a machine that can perform the integrated process of flanging and necking at the same time. Compared with the special plane shown in Figure 2, this special plane has a lot in common in basic principles. For example, the active roller is used for the active rotary motion, and the upper roller is oscillated by the cam mechanism to achieve the feed. The difference is that the specific structure of the cam feed mechanism is very different, and since the special machine is a single-head flange, the axial control mechanism of the bucket frame is increased. The working principle and process of the machine are as follows:
1) Axial positioning: When the piston in the cylinder 27 is in the rightmost position, the tail shaft 1 fixed to the piston rod and the tail plate supported by the bearing 26 on the tail shaft 1 are also in the rightmost position. At this time, the barrel frame is sleeved between the upper and lower pressing rollers 24 and 25, and the air valve is operated to make the piston left until the tail tray is sleeved into the right end of the barrel frame, and the left end of the barrel frame contacts the end surface of the side roller 3 until.
2) Flanging and necking: The motor 9 is rotated by the primary gear (the gears 10 and 8 are engaged) to rotate the spindle 5, so that the lower rear cover 25 fixed to the left end of the spindle 5 obtains the main rotary motion.
The motor 13 rotates the worm 17 by the primary belt drive (pulleys 14 and 18), and the worm wheel 16 coupled with the worm 17 is rotated slowly, so that the cam 21 coaxial with the worm wheel is also slowly rotated. Due to the action of the spring 20, the roller 22 on the roller carriage 23 always abuts against the cam. When the cam rotates and its lift increases, the roller 22 is forced to move down, and the roller frame moves down. Since the roller frame slides on the swing shaft 11, the swing shaft swings downward about the fulcrum 1 at the left end thereof. Then, the upper pressing roller 24 fixed at the right end of the oscillating uranium is pressed toward the lower pressing roller to realize the feeding motion.
During the downward swing of the oscillating shaft about the fulcrum A, the gear 12 on the yoke and the gear 7 on the rotating main shaft gradually merge to rotate the oscillating shaft, so that the upper slewing also obtains the main rotational motion.
Due to the active rotation of the upper and lower pressure rollers and the oscillating feed of the upper pressure roller, the tub frame is forced to rotate and locally deform, thereby completing the flanging and necking. As shown in the figure.
3) Returning the barrel: When the cam 21 continues to rotate and the lift is reduced, under the action of the spring, the roller frame and the roller thereon rise, the swinging shaft swings upward around the fulcrum A, and the upper pressing roller swings upward and leaves the barrel. frame. Then, the piston in the cylinder is made to the right, and the tail tray is taken out of the barrel frame, and the barrel frame can be taken out, and a working cycle ends.
In general, the rolling type flanging machine has many functions, and has strong adaptability to different metal materials and different plate thicknesses, so it is currently widely used in China. However, such machines, especially the pressure roller swing hydraulic flanger, have the disadvantage of lower flange accuracy than the squeeze flanger.
2. Extrusion type: The extrusion type cuffing machine is characterized by no rotational movement, and the cuffing action is completed by the relative movement of the two platens along the axis direction of the barrel frame. The relative movement of the two pressure plates is mostly achieved by hydraulic transmission. See Figure 7. During the burring process, the barrel wall is squeezed. In order to assist the barrel wall to withstand the pressing force, the common tire protects the barrel wall from the periphery.
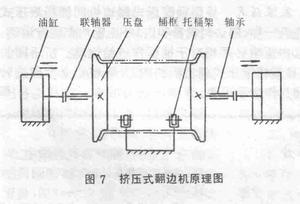
Extrusion edging machines are particularly suitable for multiple crimping, such as triple rounded buckets, due to their high flanged accuracy. In addition, due to the hydraulic drive and no rotary motion, the structure is simple and the noise is small. However, when the squeezing flange is used, the wall of the barrel is subjected to a certain pressing force, so the squeeze type burring machine cannot be used for a metal barrel having a low strength, such as an aluminum barrel. It is generally applied to steel drums with a thickness of 0.6 mm or more.
Second, the shaped bucket cuffing machine
Since the curvature around the barrel of the shaped barrel is not the same, the flange is more difficult than the barrel, so the structure of the shaped barrel flanger is more complicated than the barrel flanger. Commonly used shaped bucket flanging machines are available in both slider and hydraulic versions. For the barrel with better strength, squeeze type can also be used.
1. Slider type: In the slider type flanging machine, the flanging action is mainly performed by the slider located inside and outside the barrel frame. The principle of the slider type flange is shown in Figure 8. In the figure, the inner tube mold is fixed during the whole burring process. Its outer edge shape is the same as that of the barrel frame, and the upper part is slightly tapered to facilitate the nesting of the barrel frame. The inner and outer sliding blocks can all along the horizontal plane. slide. When working, first set the barrel frame outside the inner tube mold, and the lower end of the barrel frame is placed on the step of the inner slider, as shown in (a) of the figure. Next, slide the outer slider to the barrel frame until the barrel frame is hung from the periphery, and then slide the inner slider to the outside of the barrel until the barrel frame is finished, as shown in (b).
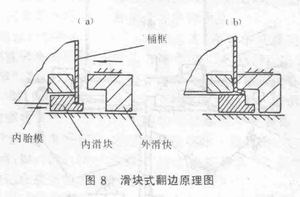
In order to ensure that the outer slider can slide along the radial direction of the barrel frame and protect the barrel frame from the entire periphery of the barrel frame, the outer slider must be composed of multiple pieces. Similarly, in order to make the inner slider slide radially along the barrel frame and to turn the end of the barrel frame outwards, the inner slide block should also be composed of multiple pieces. The number of inner and outer slider segments and the position of the dividing line depend on the cross-sectional shape of the barrel frame, and there are many options. For example, in the waist barrel flanger, the inner and outer sliders can be divided as shown in Figure 9, that is, the inner slider is divided into six pieces, and the outer slider is divided into four pieces.
The sliding of the inner and outer sliders can be achieved by a variety of mechanisms and devices. Such as crank linkage, cam mechanism, screw mechanism, ramp mechanism or hydraulic transmission and so on. In addition, since the barrel frame is subjected to an upward component force during the burring process, it is easy to lift upward. In order to prevent the barrel frame from coming to the stage, the barrel frame should be axially positioned and pressed. This action can also be done by various mechanisms or devices.
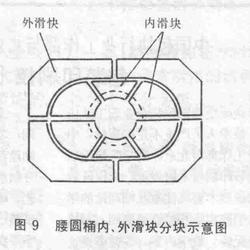
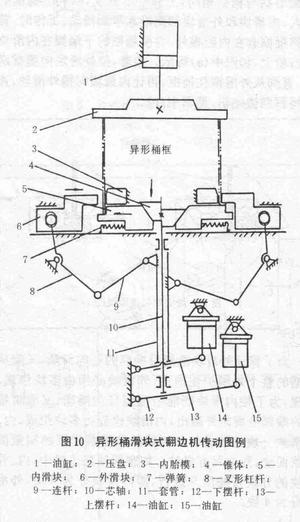
Figure 10 is a transmission diagram of the shaped bucket slider type flanger. In the figure, the left and right structures are symmetrical, and the left and right movements are simultaneous at the same time. However, in order to clearly express the transmission process, we will indicate the left half of the barrel frame to be flanged; the right half indicates the state at the end of the flange. The whole working process of the machine is described in the following four aspects.
1) Feeding and axial positioning of the barrel: When the piston in the hydraulic cylinder 1 is in the uppermost position, the pressure plate 2 fixed on the piston rod is in the uppermost position, and the barrel frame is placed under the pressure plate and sleeved The upper step of the inner tube mold 3 and the inner slider 5 is accommodated. Then, the piston is lowered, and the platen is lowered, and the barrel frame is pressed from the axial direction as shown in the left half of the figure.
2) The guard bucket: the piston in the hydraulic cylinder 14 descends, so that the upper swing rod 13 swings downward about the fulcrum of the left end thereof, and the upper end of the fork lever 8 swings toward the bucket frame through the action of the sleeve 11 and the connecting rod 9, due to The upper end of the fork lever is hinged to the outer slider 6, so that the outer slider 6 also slides in the direction of the tub until the tub is hooped from the periphery.
3) Flanging: the piston in the hydraulic cylinder 15 is descended, the hem rod 12 is swung downward about its left end fulcrum, and the mandrel 10 connected to the middle of the hem rod is moved downward, and the cone fixed at the upper end of the mandrel ( The ring cone or pyramid) 4 must move down. Through the action of the inner slider 5 and the tapered cone, the inner slide is forced to slide horizontally outside the barrel, causing the barrel to complete the flange. The middle right half.
4) Returning the barrel: Let the piston in the hydraulic cylinder 14 ascend, through the action of the upper swing rod 13, the sleeve 11 and the fork lever, the outer slider slides outward and leaves the bucket frame to return to the original position. At the same time, the piston in the cylinder 15 is advanced, the hem is swung upward, the mandrel and the cone are raised, and the inner slider slides inwardly under the action of the spring 7 to return to the original position. Then, the piston in the cylinder 1 is ascended, the pressure plate is raised, and the frame that has been turned over can be taken out.
The flanging of the shaped keg can also be achieved with a flanging device on the punch. The principle of the flange is the same as that of the slider flange described above, and the action of the outer drum and the inner slider of the flange device are all performed by the movement of the punch on the punch.
2. Rolling type: The special-shaped barrel hydraulic flanging machine is the same as the barrel rolling type flanging machine. When the flanging is turned, the barrel body and the inner and outer pressure rolls are all rotating, and the inner pressing roller must be made relative to the barrel frame. Feed movement. The difference is that the inner and outer pressure rollers of the special-shaped bucket hydraulic flanger must also be contoured with the rotating barrel.
Chamomile Oil,Pure Essential Oil Set,Orange Oil,Pure Spearmint Oil
Ji'An ZhongXiang Natural Plants Co.,Ltd. , https://www.zxnaturaloils.com